How to Select NTC Thermistors for Inrush Current Limiting
There are 3 major criteria for selecting the best NTC Thermistor inrush current limiter, surge suppressor for an application:
- Rated resistance (R25)
- Maximum permissible continuous current under rated operating conditions (Imax, DC or RMS values for AC)
- Maximum capacitance CT to be switched
The rated resistance is a measure of the damping of inrush current. Under rated operating conditions after stabilization, the maximum continuous current must under no circumstances be exceeded. Otherwise the component can be both thermally and electrically overloaded and thus destroyed.
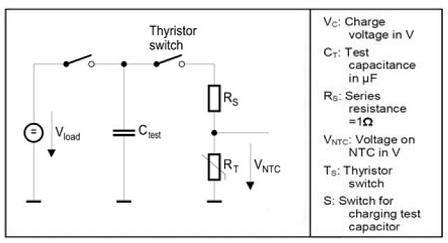
Test circuit evaluating pulse
The test method shown in the following figure is used to indicate the pulse strength. A capacitor CTdischarges across a series resistor RS and an NTC Thermistor. The charge voltage VC is selected so that the voltage VNTC applied to the Thermistor at the start of discharge is 345 V, corresponding to (230V +ΔV) x √2. The capacitance CT indicates the energy absorption capacity and thus the pulse strength of the NTC Thermistor.
The maximum capacitance to be switched represents a criterion for comparing the level and duration of the current pulse at the moment of turn-on at which the inrush current limiter can be loaded without sustaining damage.
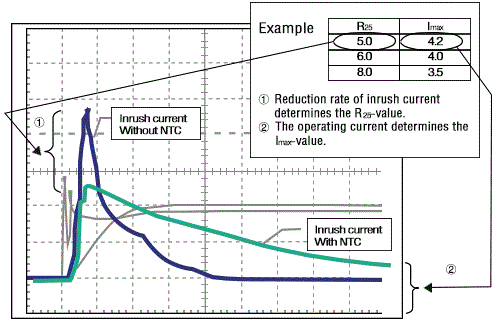
Typical power NTC Thermistor current characteristic
Knowing the capacitance CT allows an NTC thermistor to be scaled for optimum cost and geometry (space requirement). However, different CT values can be compared only if equivalent test methods are used to determine them.
A particular rated resistance R25 can be implemented in disks of different sizes. This means that for the same value of R25 different figures can be obtained for continuous load and pulse strength. So by referring to test patterns, the user can decide which inrush current limiter is best suited to the application.
As a rule of thumb, the larger the diameter of the thermistor, the higher is the current in continuous operation. This also applies to energy absorption capability and pulse strength at the moment of turn-on.
(1) Reduction rate of inrush current determines R25 value.
(2) The operating current determines Imax value.