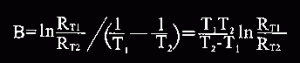NTC Thermistor Characteristics, Glossary and Definition
As defined by IEC 60539, NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistor are thermally sensitive semiconductor resistors which show a decrease in resistance as temperature increases. With -2%/K to -6%/K, the negative temperature coefficients of resistance are about ten times greater than those of metals and about five times greater than those of silicon temperature sensors.
Changes in the resistance of the NTC thermistor can be brought about either externally by a change in ambient temperature or internally by self-heating resulting from a current flowing through the device. All practical applications are based on this behavior.
NTC thermistors are made of polycrystalline mixed oxide ceramics. The conduction mechanisms in this material are quite complex, i.e. either extrinsic or intrinsic conduction may occur. In many cases NTC thermistors have a spinell structure and then show valence conduction effects.
NTC Thermistor 3 Key Characteristics
- Defined sensitivity to temperature.
- Sensitivity to electrical power input.
- Sensitivity to changes in thermal conductivity.
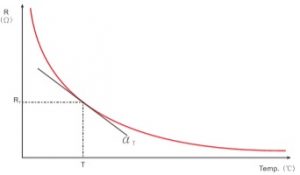
NTC Thermistor Temperature Resistance Characteristics
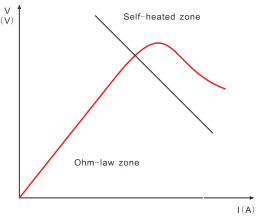
NTC Thermistor Voltage Current Characteristics
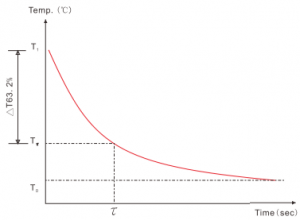
NTC Thermistor Temperature Time Characteristics
NTC Thermistor Glossary Definition
NTC Thermistor Rt — Zero Power Resistance Value
The resistance value measured at a fixed temperature by adopting sufficiently low power consumption.
NTC Thermistor R25 — Rated Zero-power Resistance Value
NTC Thermistor resistance value measured at 25C by adopting sufficiently low power consumption.
NTC Thermistor Beta Value
NTC thermistor Beta value is determined by the ceramic material and represents the slope of the R/T curve, expressed in the following formula
NTC thermistors beta calculation formula
In this formula: Rt1 is the Zero-power resistance at temperature T1; RT2 is the Zero-power resistance at temperature T2. Unless otherwise specified, Beta B value is determined from measurements made at 25C and 50C. It’s not a firm constant within the range of working temperature.
NTC Thermistor Zero Power Resistance to Temperature Coefficient
NTC thermistor temperature coefficient of resistance is defined as the relative change in resistance referred to the change in temperature.
NTC thermistors Resistance to Temperature Coefficient calculation formula
In the formula: αT-zero power resistance-temperature coefficient at temperature T RT– zero power resistance at temperature T T-temperature (expressed in K) B-B constant
NTC Thermistor Dissipation Factor δ
NTC thermistor dissipation factor δ is defined as the ratio of the change in power dissipation and the resultant change in the thermistor‘s body temperature. δ =ΔP/ΔT. δ changes in response when the ambient temperature changes, within the working temperature range.
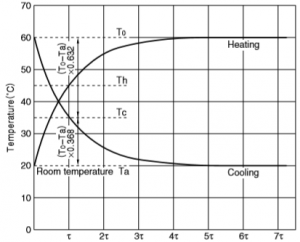
NTC Thermistor Thermal Time Constant
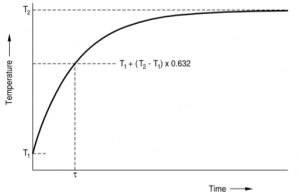
NTC thermistor Thermal Time Constant is the time required by a thermistor to change 63% of the difference between its initial and final temperature.
NTC thermistor Thermal time constant can be a crucial parameter when selecting a temperature sensor to match an application. The thermal time constant (thermal respond time) of a temperature sensor is mainly influenced by:
- Its design, e.g. sensor element, material used to assemble the sensor element in the sensor case, connection technology, housing.
- Its mounting configuration, e.g. immersed, surface-mounted.
- The environment it will be exposed to, e.g. air flow, inactive air, fluid.
Thermal Time Constant
Thermal Time Constant drawing
NTC Thermistor Maximum Stable Current
NTC thermistor Maximum Stable Current means the maximum successive current can be applied in NTC thermistor in the ambient temperature of 25oC
NTC Thermistor Resistance Temperature RT Characteristics
The dependence of the zero power resistance on NTC thermistor body temperature.