PTC Thermistor Protect the MOSFET of DC-DC Converters from Overheating
PTC Thermistor can effectively Protect the MOSFET of DC-DC Converters from Overheating by PTC thermistor resistance increasing when the temperature exceeds a desired point. PTC Detects abnormal temperature rise of the MOSFET, switches on the transistor, and decreases the FET’s gate voltage to prevent the FET from overheating. When the MOSFET temperature drops, PTC decreases the resistance, recovers its original resistance.
PTC Thermistor Converters MOSFET Temperature Protecting Outline
The MOSFET is used as the switching element of DC-DC converters or as a general-purpose current switch. When the FET is operated at a higher temperature than specified due to overloading or insufficient heat radiation, the FET can become damaged. Damage to the FET can be prevented by detecting whether it is overheating with PTC thermistor for overheat detection.
PTC thermistor for overheat detection detects the temperature of the FET itself, with the resistance of the PTC thermistor increasing when the temperature exceeds a desired point. This enables the base current to flow through the transistor and switch it on. The gate current of the FET is then bypassed to decrease the gate voltage, preventing the FET from being damaged.
Circuit Example of PTC Thermistor Protecting the MOSFET from Overheating
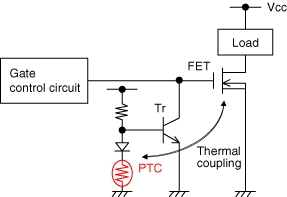
Circuit example of PTC thermistor protecting the MOSFET from overheating
FET is often used in electronic circuits as a switching element, power amplifier, etc.
When the rated temperature of the FET is exceeded because of overload or insufficient heat radiation, the FET may break down. PTC thermistor is useful to monitor the FET’s temperature. When the FET’s temperature approaches the maximum rating, PTC thermistor turns the transistor on. In this way the FET’s gate voltage decreases below its threshold level and the FET is turned off. When the FET’s temperature returns within the rating, normal operation returns. There is therefore no need to exchange protecting elements like fuses.
Roles of PTC Thermistors in Protecting DC-DC Converters MOSFET from Overheating
Detects abnormal temperature rise of the MOSFET, switches on the transistor, and decreases the FET’s gate voltage to prevent the FET from overheating.
Decreases the resistance of the PTC thermistor and unlike the thermal fuse, recovers its original resistance, when the MOSFET temperature drops.







